SEARCH
ALL NEWS
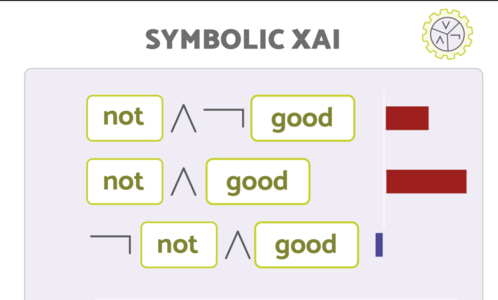
Symbolic XAI
Researchers at BIFOLD have been exploring how to make AI explain itself in the same way, people explain themselves. The team’s work focuses on making AI predictions as clear and intuitive as a human explanation.

Researcher Spotlight: Dr. Lukas Muttenthaler
What if AI could learn to see the world the way we do? BIFOLD PhD graduate Dr. Lukas Muttenthaler is pushing AI beyond raw performance, exploring representational alignment, where cognitive science meets computer vision to build machines that perceive more like humans.

Open-Source Award for DifferentiationInterface.jl
DifferentiationInterface.jl, co-developed by BIFOLD researcher Adrian Hill, wins one of France’s Open Science Awards for making cutting-edge modeling and optimization more flexible, efficient, and open.

BIFOLD supports diversity in science
On International Day of Women and Girls in Science, BIFOLD celebrates its diverse research community.

Fraunhofer HHI wins prestigious Best Paper Award for XAI research
The AI Department at Fraunhofer HHI has received the 2025 Information Fusion Best Paper Award for its roadmap-defining paper on Explainable AI. Co-authored by department head and BIFOLD Fellow Wojciech Samek, the work outlines key challenges and directions for future XAI research.

Ask Agent-BigEarth
Begüm Demir, Professor of Remote Sensing Image Analysis at TU Berlin and research group lead at BIFOLD (Berlin Institute for the Foundations of Learning and Data), has secured one of the coveted Proof of Concept grants from the European Research Council (ERC). These grants aim to bridge the gap between fundamental research and practical applications, helping to transform pioneering research results into tangible societal or commercial benefits.
How the Brain Organizes Memories
A new study, published in Nature, reveals, for the first time, how the brain stores memory content and its context in two largely separate groups of nerve cells. Among those involved in the international research led by the University of Bonn was Dr. Johannes Niediek, a researcher at BIFOLD / TU Berlin, ML Group.

Test-of-Time Award for Konrad Rieck
Congratulations to BIFOLD Research Group Lead Konrad Rieck and his former colleagues. The Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC) awarded the scientists the Test-of-Time Award for their publication "CUJO: Efficient Detection and Prevention of Drive by Download Attacks" (2010).

Quantum Physicist Jens Eisert Joins BIFOLD as Fellow
Theoretical physicist Jens Eisert brings expertise in quantum computing and AI to BIFOLD’s Fellowship Program. His appointment advances Berlin’s efforts to link quantum research with machine learning.

Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize awarded to Klaus-Robert Müller
Prof. Dr. Klaus-Robert Müller, co-director of BIFOLD and head of the Machine Learning Group at TU Berlin is honored with the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize 2026, considered the highest honor for researchers in Germany. He is regarded as a pioneer of machine learning and has been driving this important area of artificial intelligence (AI) since 1989. His work combines excellence in formal mathematical reasoning with a strongly application-oriented approach.

